

The smooth ER is named for its relatively smooth exterior as comparedto the rough ER, which is covered in ribosomes on its cytoplasmic side. The ER is divided into two types, the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) and the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). In a nutshell, the endoplasmic reticulum is tasked with transporting materials within the cell. This membrane system divides the internal sac space of the ER, the lumen, from the cytosol.
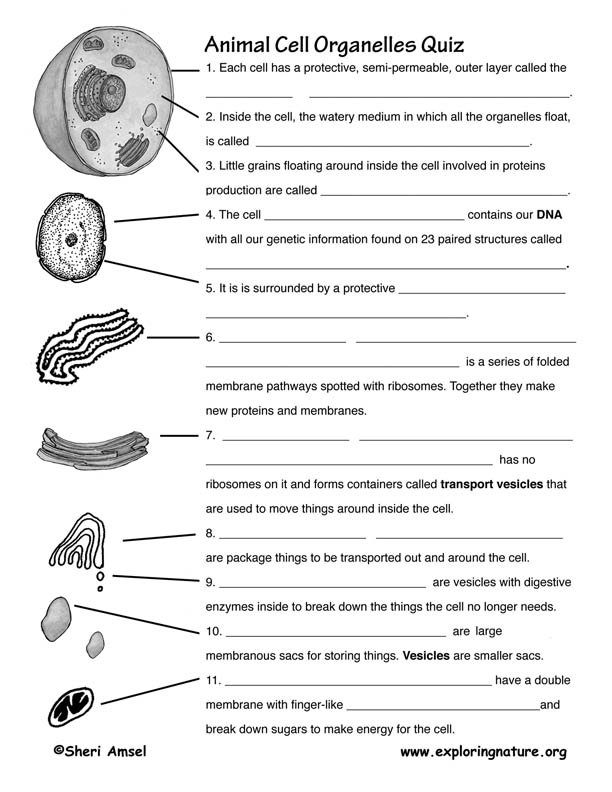
The endoplasmic reticulum is a major manufacturing and transportation center of the cell with an intricate membrane system consisting of a network of tubules and sacs. Manufacturing Organelle: The Endoplasmic Reticulumįor AP® Biology you will need to know the ER. This membrane extends onto the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER), which we’ll touch upon next. The nucleus as a whole is enclosed in a nuclear envelope, which is a double membrane that holds the content of the nucleus in place. Most of the cell’s ribosomal RNA synthesis activities take place in a cell organelle called the nucleolus, which is a small compartment of the nucleus. It is here that DNA is stored and RNA is synthesized, amongst other operations. The nucleus is often located near the center of the cell. All but a few cell organelles rely on the nucleus for guidance. The nucleus is the center of all cell functions. We will start with the nucleus both plant and animal cells have this organelle. Image Source: Wikimedia Commons Center of Operations: The Nucleus Image Source: Wikimedia Commons Figure 2: A diagram of the animal cell. We will also touch up on how organelles are often strategically positioned. We’ll look at which organelles they share, which ones they do not, why this is the case and the function of all these organelles. A eukaryotic cell is a type of cell that possesses a distinct membrane-bound nucleus, whereas a prokaryotic cell does not have a nucleus.Here we will focus on eukaryotic cells.įor the purpose of this AP® Biology crash course, we will take a tour through plant and animal cells. For Advanced Placement (AP) Biology there are two main eukaryotic cell types, the animal cell and the plant cell, which you need to understand well. Cell organelles perform important tasks to maintain normal cell functions including cell division. These components are what we call cell organelles. All cells are self-sustaining entities with different tasks divvied up to different components of the cell.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
